Introduction
LASER is a term used to describe Light Amplification from Stimulated emission of radiation. Laser is generated by a particular procedure inside the laser device that creates the controlled emission of radiation forms of light. Laser is usually available in a single color and is available as light-like beams. Lasers were created by scientist Gordon Gould in 1958, and the first operational model was developed in 1960.They have been in use throughout Europe as well as America for over 40 years and have been employed in dermatology surgical. Ophthalmology, physical medicine, and rehabilitation. Lasers are used by physiotherapists to ease pain and speed up healing, and reduce swelling. [1]
differentiates Between Low-Level Laser Therapy and High Power Laser Therapy
A laser’s output power lower than 0.5 Watts is classified as low-level laser Therapy (LLLT) ( Class III lasers in the USA), while lasers that have power outputs more significant than 500 mW (or 0.5 Watts are known as HPLT (High Power Laser Therapy HPLT (Class IV lasers in the USA). HPLT produces thermal heat on the skin’s surface because of its greater energy density (irradiance). LLLT is sometimes described as “Cold Lasers” since they don’t cause the sensation of heating when treated. [2]
Production of Laser
Laser devices comprise an optical chamber, or chamber that houses the active media for which laser is the name. The section is equipped with mirrors on both ends that are aligned to each other within the same distance of light. One mirror is open. Energy or electricity is injected into the medium, which stimulates it. The atoms of the active medium are reflections back and forth across the mirrors inside the chambers. This causes more stimulation of the atoms inside the medium. The laser light is then emitted via the reflective portion of the mirror. The process of producing light follows the following manners:
1.Electron is then pumped to an increased energy level.
2.Pumping level is not stable, so the electron rapidly jumps to a lower level.
3.Electron reduces in a more sluggish energy level and releases photons.
4.Light and an electron at an energy level that is excited creates two photons with identical length and frequency.
5.Mirror is a mirror that reflects photons or laser light. [1]
Characteristics of Laser
Because of the specific nature of laser manufacturing, it has its own particular characteristics.
1. Monochromaticity “mono” is a singular. ‘Chromaticity’ meaning color. Lasers emit one pure color since it has a single wavelength.
2. Coherence Laser rays synchronization with one another. The crest and the trough of rays are identical to each other.
3. Collimation It’s also known as non-divergence. Laser rays move parallel to one another. [1]
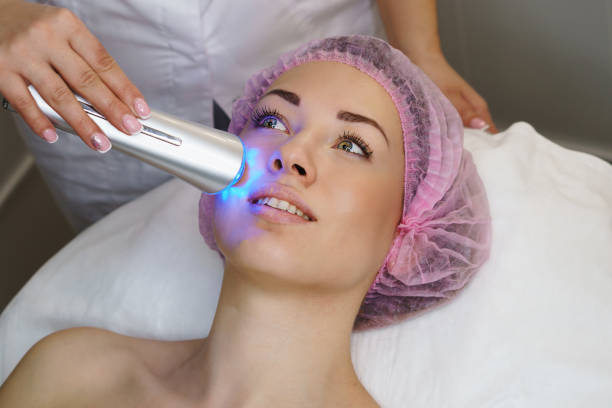
What is Laser work?
If the source of light is positioned against the skin’s surface, radiation travels through a few centimeters before being absorbed by mitochondria. The energy triggers a range of positive physiological responses that lead to standard cell structure and function recovery but at a higher rate—targeted in cytochrome oxidase. The high-power diode laser may aid in respiration and consequently provide an effective treatment for performance. [2]
[3]
Indications
The physiotherapists employ HPLT primarily based on the notion that cells stimulated by the laser can speed up the healing process.
Class IV high-intensity hot laser therapy (high-intensity laser therapy) is a treatment for a variety of illnesses, such as:
- Osteoarthritis in the hip, knee, and ankle
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Syndromes of shoulder impingement
- Shoulder or hip bursitis
- Lower rear disc degeneration
- Disc herniation of the disc
- Sciatica
- Tendonitis
- The tennis elbow
- Plantar fasciitis
- Sprain
- Tenosynovitis
- Trigger finger
- Ulcers
- Incisions [1]
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Tumor
- Hemorrhage
- Pacemaker
- Thrombosis[1]
Precautions
*Should wear protective glasses for lasers or goggles
Inappropriate use of the glasses is more risky than use since they could give a false impression of security.
*Laser equipment needs to be stored in a safe area with limited access to prevent accidental exposure
Avoid reflections of lasers from mirror surfaces
Avoid exposing eyes and fontanels that are not closed by young children. [1]
Evidence
The study results from 2018 called “Effectiveness of high-intensity laser therapy in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials” concluded that HILT treatments for neck and back discomfort significantly reduced scores for disability and pain in comparison to controls. The study also noted that further study designs that included larger samples with long-term follow-up are required to evaluate the efficacy of each laser region of treatment and the comparators.